The Federal in Federalism Worksheet embarks on an in-depth exploration of the intricate web of federalism, unraveling its foundational principles, the division of powers between federal and state governments, and its profound impact on American society. As we delve into this comprehensive resource, we will dissect the complexities of federalism, gaining a deeper appreciation for its historical evolution and contemporary relevance.
This worksheet serves as a roadmap, guiding us through the multifaceted nature of federalism, its role in shaping American identity, and the ongoing debates that surround its interpretation and implementation. By engaging with this material, we will emerge with a comprehensive understanding of the federal system, its strengths, and its challenges, equipping us to navigate the complexities of contemporary federalism in an informed and nuanced manner.
Defining Federalism: The Federal In Federalism Worksheet
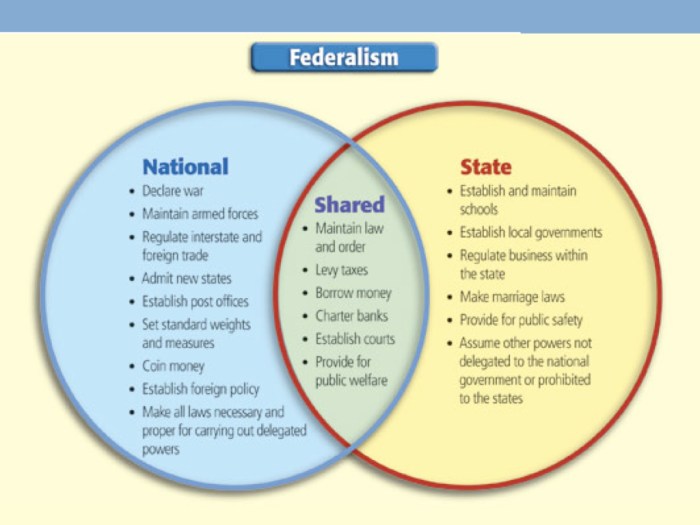
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central government and several regional governments. Each level of government has its own set of responsibilities and powers.
Federal systems are often created when a group of independent states agree to unite under a single government. The central government is typically responsible for matters that affect the entire country, such as foreign policy, defense, and interstate commerce. The regional governments are responsible for matters that are more local in nature, such as education, healthcare, and law enforcement.
Examples of Federal Systems
There are many examples of federal systems around the world. Some of the most well-known include:
- United States
- Canada
- Australia
- Germany
- Switzerland
Division of Powers
In a federal system, the division of powers between the central and regional governments is typically set out in a written constitution. The constitution will specify which powers are exclusive to the central government, which powers are exclusive to the regional governments, and which powers are shared by both levels of government.
The division of powers in a federal system is designed to ensure that neither the central government nor the regional governments become too powerful. It also helps to protect the rights of individuals and minorities.
The Role of the Federal Government
The federal government is the central governing authority of a federation. It possesses specific powers and responsibilities, distinct from those of the individual states or provinces that comprise the federation. These powers are typically Artikeld in a constitution or other foundational document.
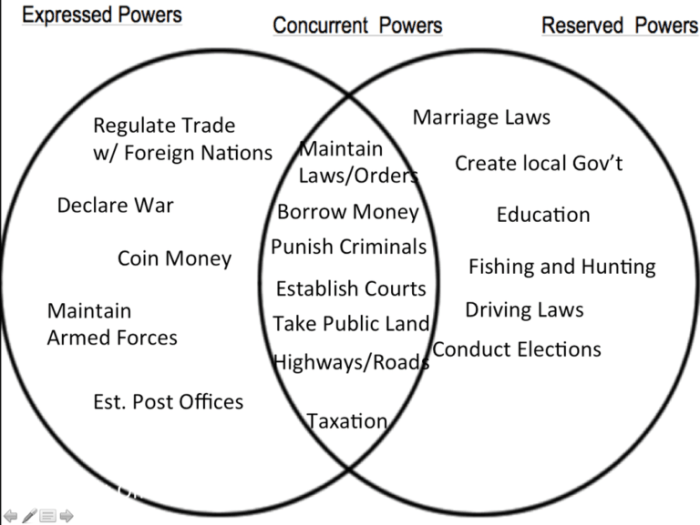
Exclusive Powers
Exclusive powers are those that are solely exercised by the federal government. These powers are often essential to maintaining the integrity and sovereignty of the nation. Some common exclusive powers include:
- Defense and national security
- Foreign policy and diplomacy
- Regulation of interstate commerce
- Coining and printing money
- Establishing and maintaining a postal service
Concurrent Powers
Concurrent powers are those that are shared between the federal government and the states. Both levels of government can exercise these powers, although the federal government may have ultimate authority in the event of a conflict. Some common concurrent powers include:
- Taxation
- Education
- Public health
- Law enforcement
- Environmental protection
Reserved Powers
Reserved powers are those that are exclusively reserved for the states. These powers are typically related to local matters and are not delegated to the federal government. Some common reserved powers include:
- Regulation of intrastate commerce
- Education
- Public health
- Law enforcement
- Marriage and family law
The Role of State Governments
State governments play a crucial role in the federal system, exercising powers and responsibilities that are distinct from those of the federal government. They possess significant authority over matters that directly impact the lives of citizens within their respective jurisdictions.
Powers and Responsibilities of State Governments
State governments are vested with a wide range of powers and responsibilities, including:
- Education: Establishing and regulating public education systems, including K-12 schools and higher education institutions.
- Public health and safety: Protecting the health and well-being of citizens through regulations, public health programs, and law enforcement.
- Transportation: Constructing and maintaining roads, bridges, and public transportation systems within their borders.
- Environmental protection: Regulating land use, air and water quality, and conservation efforts to preserve the environment.
- Law enforcement and criminal justice: Establishing and enforcing laws, operating police and judicial systems, and maintaining prisons.
Relationship between State Governments and the Federal Government
The relationship between state governments and the federal government is complex and multifaceted. While the federal government retains ultimate authority over matters of national importance, state governments possess significant autonomy in areas delegated to them by the Constitution.
This relationship is governed by principles such as:
- Federal supremacy: Federal laws and regulations prevail over state laws in cases of conflict.
- Reserved powers: State governments retain all powers not explicitly granted to the federal government by the Constitution.
- Cooperative federalism: Both levels of government often collaborate and share responsibilities in areas such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
The Impact of Federalism on American Society
Federalism has profoundly shaped American society and its values. The division of powers between the federal government and state governments has fostered a unique balance between unity and diversity.Federalism has allowed for a diverse array of cultures and perspectives to flourish within the United States.
States have the autonomy to establish their own laws and regulations, reflecting the values and priorities of their citizens. This decentralized approach has encouraged innovation and experimentation, leading to a rich tapestry of social and economic policies.
Benefits of Federalism
Federalism offers several key benefits to American society:
-
-*Preservation of local autonomy
States retain significant control over matters that directly affect their citizens, such as education, healthcare, and criminal justice.
-*Protection of minority rights
The federal government serves as a safeguard against the potential tyranny of the majority at the state level, ensuring that the rights of all citizens are protected.
-*Experimentation and innovation
States are free to experiment with different approaches to governance, providing a testing ground for new ideas that can later be adopted at the federal level.
Challenges of Federalism
Despite its benefits, federalism also presents certain challenges:
-
-*Intergovernmental conflict
Federal and state governments may clash over policy issues, leading to delays or deadlocks in decision-making.
-*Inequality between states
The distribution of resources and opportunities can vary significantly between states, resulting in disparities in economic development and social welfare.
-*Erosion of federal authority
In recent decades, there has been a trend towards the expansion of federal power at the expense of state authority, raising concerns about the preservation of local autonomy.
Historical Examples
Federalism has played a pivotal role in shaping major events in American history:
-
-*The Civil War
The conflict between the Union and the Confederacy stemmed in part from differing interpretations of federalism, with the South advocating for states’ rights and the North prioritizing national unity.
-*The New Deal
President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal programs expanded the role of the federal government in economic and social welfare, while still respecting the autonomy of states.
-*The Civil Rights Movement
The federal government played a crucial role in enforcing the civil rights of African Americans, despite resistance from some states.
Contemporary Issues in Federalism
Federalism in the United States continues to be a subject of debate and controversy. Key issues include the balance of power between the federal and state governments, the role of the Supreme Court in interpreting the Constitution, and proposals for reforming the federal system.
The Role of the Supreme Court, The federal in federalism worksheet
The Supreme Court plays a critical role in interpreting the Constitution and resolving disputes between the federal and state governments. In recent years, the Court has issued several important rulings that have shaped the balance of power between the two levels of government.
For example, in National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius(2012), the Court struck down the individual mandate of the Affordable Care Act, arguing that it exceeded Congress’s power under the Commerce Clause. This decision was a significant victory for states’ rights and limited the federal government’s ability to regulate economic activity.
Helpful Answers
What is federalism?
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and constituent political units, such as states or provinces.
What are the advantages of federalism?
Federalism allows for diversity and local autonomy while also providing a framework for national unity and cooperation.
What are the challenges of federalism?
Federalism can lead to conflicts between the central and constituent governments, as well as imbalances in power and resources.