Myasthenia gravis system disorder template provides a comprehensive overview of this autoimmune disorder, encompassing its definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, management strategies, and emerging therapies. This template serves as an invaluable resource for healthcare professionals seeking to enhance their understanding and clinical approach to myasthenia gravis.
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness and fatigability. It arises from a disruption in neuromuscular transmission due to the presence of antibodies that target acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. The prevalence of myasthenia gravis is estimated to be around 1 in 20,000 individuals, with a higher incidence among women than men.
1. Myasthenia Gravis
Definition and Overview
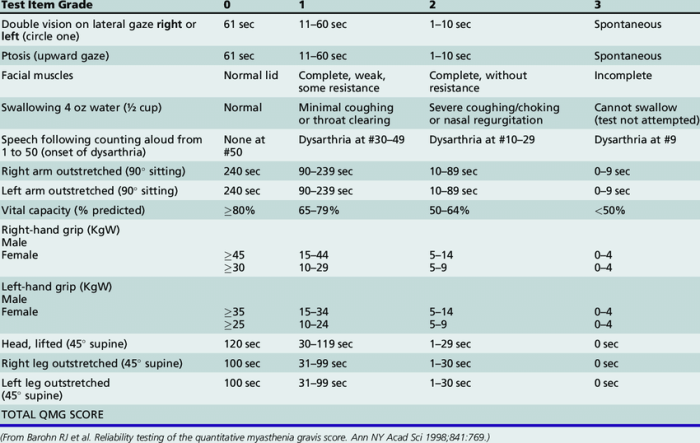
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune neuromuscular disorder characterized by muscle weakness and fatigability. It is caused by a disruption in the normal communication between nerves and muscles, leading to impaired muscle function.
The history of myasthenia gravis dates back to the 17th century, with the first documented case described in 1672. However, it was not until the 20th century that significant progress was made in understanding the underlying mechanisms of the disease.
Myasthenia gravis is a relatively rare condition, affecting approximately 1 in 10,000 people worldwide. It can occur at any age, but the peak incidence is between the ages of 20 and 40 years. Women are more commonly affected than men.
2. Causes and Risk Factors

Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder, meaning that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues. In the case of myasthenia gravis, the immune system produces antibodies that target the acetylcholine receptors on the surface of muscle cells.
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in neuromuscular transmission. When a nerve impulse reaches the neuromuscular junction, acetylcholine is released from the nerve terminal and binds to acetylcholine receptors on the muscle cell. This binding triggers a cascade of events that leads to muscle contraction.
In myasthenia gravis, the antibodies bind to and block the acetylcholine receptors, preventing acetylcholine from binding and initiating muscle contraction. This leads to muscle weakness and fatigability, which can range from mild to severe.
Types of Myasthenia Gravis, Myasthenia gravis system disorder template
- Ocular myasthenia gravis:Affects only the muscles around the eyes, causing drooping eyelids (ptosis) and double vision (diplopia).
- Generalized myasthenia gravis:Affects muscles throughout the body, including the limbs, neck, and respiratory muscles.
- Bulbar myasthenia gravis:Affects the muscles of the face, throat, and neck, leading to difficulty speaking, swallowing, and breathing.
3. Signs and Symptoms: Myasthenia Gravis System Disorder Template
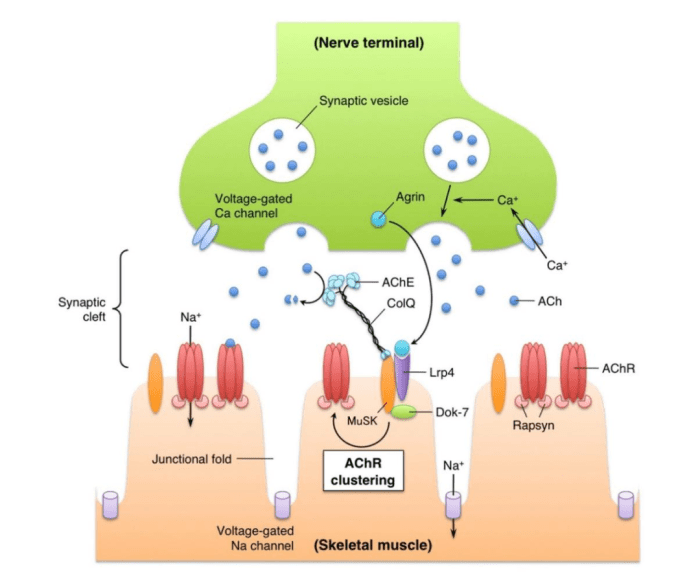
The classic symptoms of myasthenia gravis are muscle weakness and fatigability. Muscle weakness is typically worse in the morning and improves slightly later in the day. Fatigability refers to the tendency for muscles to become weaker with repeated use.
Muscle weakness in myasthenia gravis can affect any muscle group in the body, but it is most commonly seen in the following areas:
- Eye muscles (ptosis, diplopia)
- Facial muscles (difficulty smiling, chewing)
- Neck muscles (difficulty holding up the head)
- Limb muscles (weakness in the arms and legs)
- Respiratory muscles (difficulty breathing)
FAQ Compilation
What is the primary cause of myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenia gravis is primarily caused by an autoimmune response that leads to the production of antibodies that block or destroy acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction, impairing nerve impulse transmission to muscles.
What are the common symptoms of myasthenia gravis?
Characteristic symptoms of myasthenia gravis include muscle weakness and fatigability, which may initially affect the eyes (ptosis, diplopia) and gradually involve other muscle groups, leading to difficulty with chewing, swallowing, speaking, and breathing.
How is myasthenia gravis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of myasthenia gravis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, electrodiagnostic studies (electromyography), and serological testing to detect the presence of acetylcholine receptor antibodies.
What are the treatment options for myasthenia gravis?
Treatment strategies for myasthenia gravis include medications such as cholinesterase inhibitors to enhance neuromuscular transmission, immunosuppressants to suppress antibody production, and thymectomy (surgical removal of the thymus gland) in certain cases.
What is the prognosis for myasthenia gravis?
The prognosis for myasthenia gravis varies depending on the severity and type of the disorder. With appropriate treatment and management, many patients can achieve remission or significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life.
