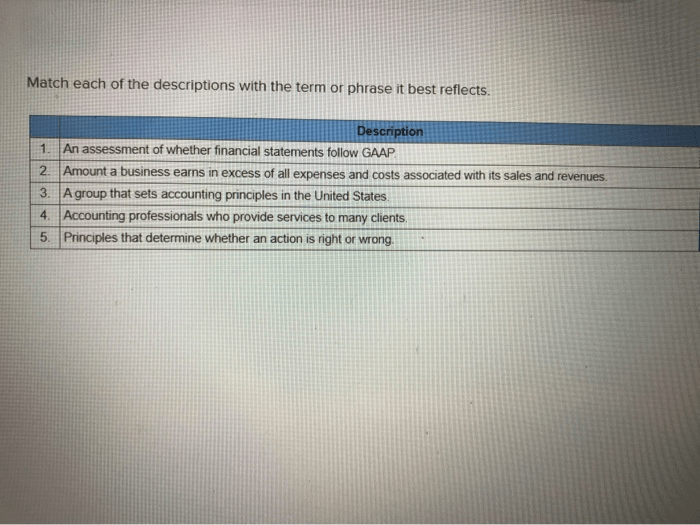
An assessment of whether financial statements follow GAAP is a crucial process in ensuring the accuracy, transparency, and reliability of financial reporting. GAAP, or Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, serves as the guiding framework for financial statement preparation, ensuring consistency and comparability across different organizations.
Assessing GAAP compliance involves evaluating whether financial statements adhere to these established principles and standards, providing assurance to stakeholders about the credibility of the reported financial information.
This assessment process plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of financial reporting, safeguarding investors, creditors, and other users of financial statements. By adhering to GAAP, organizations can enhance the credibility of their financial information, foster trust among stakeholders, and facilitate informed decision-making.
Introduction
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) provide a framework for financial reporting that ensures consistency, transparency, and comparability of financial statements. Assessing whether financial statements follow GAAP is crucial for various stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and regulators, to make informed decisions based on accurate and reliable financial information.
Methods of Assessment

There are several methods used to assess GAAP compliance, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Analytical Procedures:Comparing financial ratios and trends to industry benchmarks or prior periods to identify potential anomalies or inconsistencies.
- Inquiry of Management:Obtaining written or verbal representations from management regarding their compliance with GAAP.
- Inspection of Documents:Examining supporting documentation, such as invoices, contracts, and bank statements, to verify the accuracy of financial statement assertions.
- Observation of Processes:Witnessing key accounting processes, such as inventory counting or cash handling, to assess the effectiveness of internal controls.
- Recalculation of Accounts:Independently performing calculations to verify the accuracy of financial statement balances.
Key Areas of Assessment: An Assessment Of Whether Financial Statements Follow Gaap

The key areas of financial statements that are subject to GAAP requirements include:
- Balance Sheet:Assets, liabilities, and equity
- Income Statement:Revenues, expenses, and net income
- Statement of Cash Flows:Cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities
- Statement of Changes in Equity:Changes in capital, retained earnings, and other equity components
- Notes to Financial Statements:Additional disclosures and explanations of accounting policies and significant events
Reporting and Disclosure
The results of GAAP assessments should be reported and disclosed to relevant stakeholders, such as investors and regulators. Common types of reports include:
- Management’s Discussion and Analysis (MD&A):A narrative discussion of the company’s financial performance and condition, including any significant deviations from GAAP.
- Auditor’s Report:An independent auditor’s opinion on the fairness of the financial statements and their compliance with GAAP.
- Form 10-K:An annual report filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) that includes detailed financial statements and other information.
Non-compliance with GAAP reporting requirements can have serious consequences, such as regulatory penalties, loss of investor confidence, and legal liability.
Benefits and Limitations

Benefits of GAAP Assessments, An assessment of whether financial statements follow gaap
- Enhanced credibility and reliability of financial statements
- Improved comparability of financial performance across companies and industries
- Increased investor confidence and access to capital
- Reduced risk of financial fraud and misstatement
Limitations of GAAP Assessments
- Costly and time-consuming process
- May not detect all instances of non-compliance
- Can be subjective and dependent on the auditor’s judgment
To address these limitations, it is important to establish a comprehensive assessment plan, engage experienced professionals, and continuously monitor and improve the assessment process.
Essential FAQs
What are the benefits of assessing financial statements for GAAP compliance?
Assessing financial statements for GAAP compliance enhances the credibility and reliability of financial reporting, facilitates comparability across different organizations, and safeguards the interests of stakeholders.
What are the key areas of financial statements that are subject to GAAP requirements?
GAAP requirements encompass various aspects of financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, statement of cash flows, and statement of changes in equity.
What are the implications of non-compliance with GAAP reporting requirements?
Non-compliance with GAAP reporting requirements can result in financial misstatement, loss of investor confidence, regulatory penalties, and damage to the organization’s reputation.