Embark on a comprehensive exploration of Topic 1.1 Introduction to Ecosystems Answer Key, a meticulously crafted guide that unravels the complexities of ecological systems. This answer key provides an in-depth understanding of the fundamental concepts, structures, functions, and dynamics of ecosystems, empowering readers with a profound appreciation for the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
Delving into the intricacies of ecosystems, this answer key elucidates the interplay between biotic and abiotic components, showcasing the remarkable diversity of ecosystems that grace our planet. From the lush forests to the vast oceans, each ecosystem harbors unique characteristics that shape the distribution and interactions of its inhabitants.
1. Ecosystems
An Overview
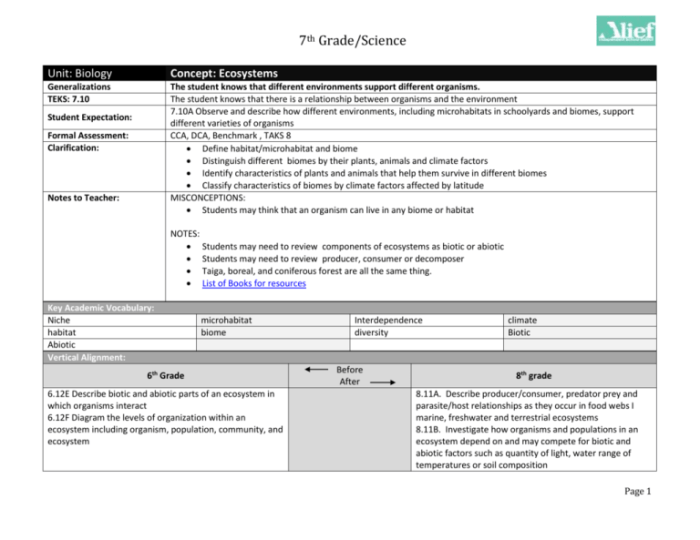
Ecosystems are complex systems that include all living organisms (biotic components) and their physical surroundings (abiotic components) in a particular area. These components interact and influence each other, creating a dynamic and interconnected web of life.
Ecosystems vary greatly in size and complexity, from small ponds to vast oceans. They can be classified into different types based on their dominant vegetation, climate, or geographic location, such as forests, grasslands, deserts, and marine ecosystems.
Ecosystems are essential for life on Earth. They provide a wide range of services, including food, water, air purification, and climate regulation. They also support biodiversity and play a crucial role in maintaining the planet’s ecological balance.
2. Ecosystem Structure, Topic 1.1 introduction to ecosystems answer key
Ecosystems have a hierarchical structure, with different levels of organization from individuals to populations to communities.
- Individualsare single organisms of a particular species.
- Populationsare groups of individuals of the same species living in the same area.
- Communitiesare assemblages of different populations living together in a particular area.
Within communities, each species occupies a specific ecological niche, which defines its role and interactions with other species.
Abiotic factors, such as climate, soil conditions, and water availability, also play a significant role in shaping ecosystem structure by influencing the distribution and abundance of organisms.
3. Ecosystem Function
Ecosystems function through the flow of energy and nutrients. Energy enters the ecosystem through photosynthesis, performed by plants and other photosynthetic organisms. This energy is then passed along through food webs as organisms consume each other.
- Producers(plants) convert sunlight into energy-rich molecules through photosynthesis.
- Consumers(animals) obtain energy by consuming producers or other consumers.
- Decomposers(bacteria and fungi) break down dead organisms and waste products, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Ecosystems also provide a variety of ecosystem services, such as air and water purification, pollination, and climate regulation, which benefit human well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions: Topic 1.1 Introduction To Ecosystems Answer Key
What is the significance of ecosystems for life on Earth?
Ecosystems provide essential life-supporting services such as regulating climate, purifying air and water, and providing food, shelter, and resources for all living organisms.
How do abiotic factors influence ecosystem structure?
Abiotic factors such as climate, soil conditions, and topography shape the distribution and abundance of organisms within an ecosystem, influencing the overall structure and dynamics of the system.
What is the role of decomposers in ecosystem function?
Decomposers break down dead organisms and organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem. This process is crucial for nutrient cycling and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.