Advanced Hardware Lab 10-1: Identify Steps of Laser Printing embarks on an in-depth exploration of the sophisticated technology behind laser printing. This intricate process involves a series of meticulously orchestrated steps, each contributing to the creation of high-quality prints with remarkable precision.
Delving into the core principles of laser printing, we will uncover the fundamental concepts of laser scanning, electrostatic charging, toner transfer, and fusing. These fundamental elements provide the foundation for understanding the intricate workings of a laser printer.
Introduction

Laser printing is a digital printing technology that uses a laser beam to create an electrostatic image on a photosensitive drum. The image is then transferred to paper using toner particles, which are attracted to the charged areas on the drum.
Laser printing is widely used for producing high-quality documents and graphics, such as business documents, marketing materials, and technical drawings.
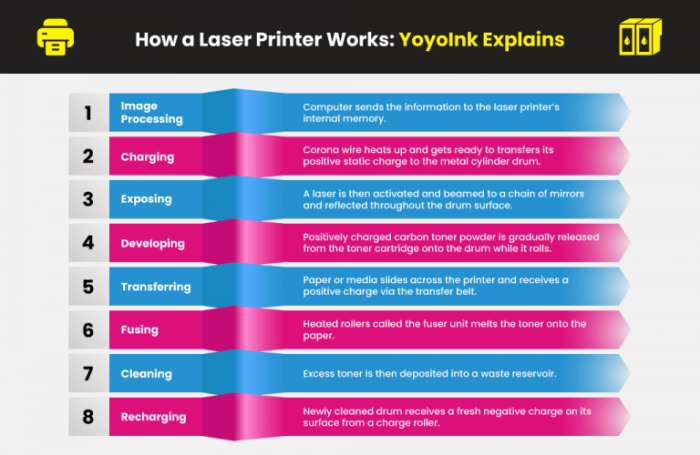
The laser printing process involves several key steps:
- Preparing the print data
- Transferring the image to the print drum
- Applying toner to the print drum
- Transferring toner to the paper
- Fusing the toner to the paper
Laser Printing Process
Laser Scanning
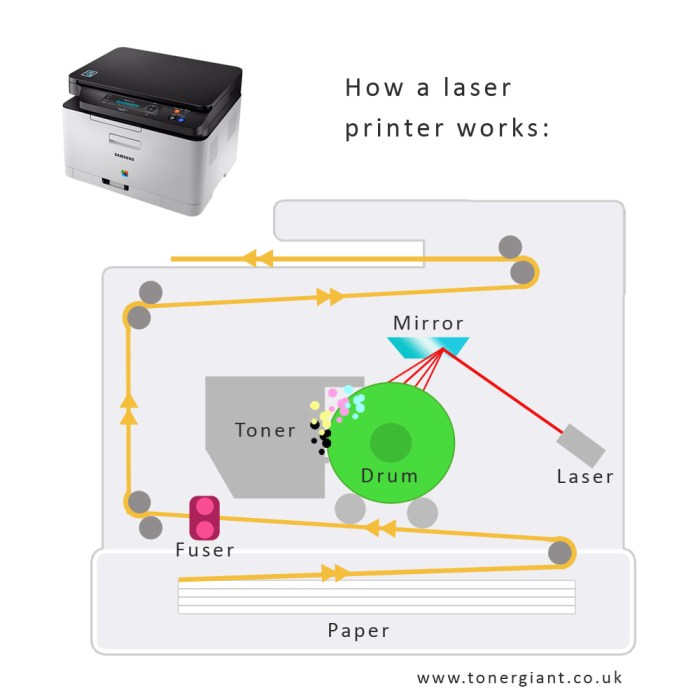
The laser printing process begins with laser scanning. A laser beam is directed onto a rotating print drum, which is coated with a photosensitive material. The laser beam creates an electrostatic image on the drum by selectively charging different areas of the surface.
The charged areas will attract toner particles, while the uncharged areas will repel them.
Electrostatic Charging
After the laser has scanned the print drum, the drum is electrostatically charged. This process creates a positive charge on the surface of the drum, which attracts negatively charged toner particles.
Toner Transfer
The toner cartridge contains fine particles of toner, which are made of a mixture of plastic and carbon. The toner particles are attracted to the charged areas on the print drum and adhere to them.
Fusing
The final step in the laser printing process is fusing. The toner particles are heated and fused to the paper using a heated roller. This process permanently bonds the toner to the paper, creating a high-quality printed image.
Laser Printer Components: Advanced Hardware Lab 10-1: Identify Steps Of Laser Printing
Laser Unit
The laser unit is the heart of a laser printer. It generates the laser beam that is used to create the electrostatic image on the print drum.
Print Drum
The print drum is a rotating cylinder that is coated with a photosensitive material. The laser beam scans the print drum and creates an electrostatic image on its surface.
Toner Cartridge
The toner cartridge contains the toner particles that are used to create the printed image. The toner particles are attracted to the charged areas on the print drum and adhere to them.
Fuser
The fuser is a heated roller that fuses the toner particles to the paper. This process permanently bonds the toner to the paper, creating a high-quality printed image.
Steps of Laser Printing
Preparing the Print Data, Advanced hardware lab 10-1: identify steps of laser printing
The first step in laser printing is to prepare the print data. This involves converting the digital document into a format that can be understood by the printer. The print data is then sent to the printer’s memory.
Transferring the Image to the Print Drum
The next step is to transfer the image to the print drum. The laser beam scans the print drum and creates an electrostatic image on its surface. The charged areas on the drum will attract toner particles, while the uncharged areas will repel them.
Applying Toner to the Print Drum
The toner cartridge contains fine particles of toner, which are made of a mixture of plastic and carbon. The toner particles are attracted to the charged areas on the print drum and adhere to them.
Transferring Toner to the Paper
Once the toner has been applied to the print drum, it is transferred to the paper. The paper is passed through a series of rollers, which press the toner particles onto the paper.
Fusing the Toner to the Paper
The final step in the laser printing process is fusing. The toner particles are heated and fused to the paper using a heated roller. This process permanently bonds the toner to the paper, creating a high-quality printed image.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Printing
Advantages
- High print quality
- Fast print speeds
- Cost-effectiveness
Disadvantages
- High initial cost
- Limited color printing capabilities
Applications of Laser Printing
Laser printing is commonly used for producing high-quality documents and graphics, such as:
- Business documents
- Marketing materials
- Technical drawings
Questions Often Asked
What is the fundamental principle behind laser printing?
Laser printing utilizes a laser beam to create an electrostatic image on a print drum, which attracts toner particles that are then transferred to paper and fused with heat.
What are the key advantages of laser printing?
Laser printing offers high print quality, fast print speeds, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
What are the potential disadvantages of laser printing?
Laser printers can have a higher initial cost compared to other printing technologies and may have limited color printing capabilities.