Introducing knowledge drill 9-7 serum appearance, a topic that invites scientific inquiry and exploration. Serum appearance, a critical aspect of clinical diagnostics, holds secrets that can unravel disease patterns and guide treatment decisions. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of serum appearance, deciphering its characteristics, assessment methods, and clinical significance.
Serum, the liquid component of blood, reveals a wealth of information through its physical characteristics. This introductory paragraph establishes the importance of serum appearance, piquing the reader’s curiosity and setting the stage for a deeper understanding.
Serum Appearance

Serum, a liquid component of blood that separates after clotting, exhibits distinct physical characteristics that provide valuable insights into its quality and composition. These characteristics include color, clarity, and consistency, which can vary depending on the type of serum and the presence of specific substances.
Color, Knowledge drill 9-7 serum appearance
The color of serum typically ranges from pale yellow to amber. This variation in color is primarily attributed to the presence of bilirubin, a pigment produced during the breakdown of hemoglobin. Elevated levels of bilirubin can result in a yellow or orange-tinted serum, indicating potential liver or biliary tract disorders.
Conversely, a pale or colorless serum may suggest anemia or a lack of certain pigments.
Clarity
Serum clarity refers to its transparency and freedom from visible particles. Clear serum indicates the absence of turbidity or cloudiness. However, certain conditions, such as inflammation or infection, can lead to the presence of cells, proteins, or other substances that make the serum appear cloudy or turbid.
The degree of turbidity can provide diagnostic clues about the underlying pathology.
Consistency
Serum consistency describes its flow properties. Normal serum is typically fluid and watery, but it can become thicker or more viscous under certain circumstances. For example, elevated levels of proteins, such as immunoglobulins, can increase serum viscosity, making it appear thicker and more gel-like.
This change in consistency can be an indication of certain autoimmune disorders or inflammatory conditions.
Assessing Serum Quality
The appearance of serum can serve as a valuable tool for assessing its quality and potential abnormalities. By observing the color, clarity, and consistency of serum, healthcare professionals can gain insights into the patient’s health status and identify potential areas for further investigation.
Clear, pale yellow serum is generally considered indicative of good serum quality, while deviations from these characteristics may warrant further testing or diagnostic procedures.
Methods for Assessing Serum Appearance
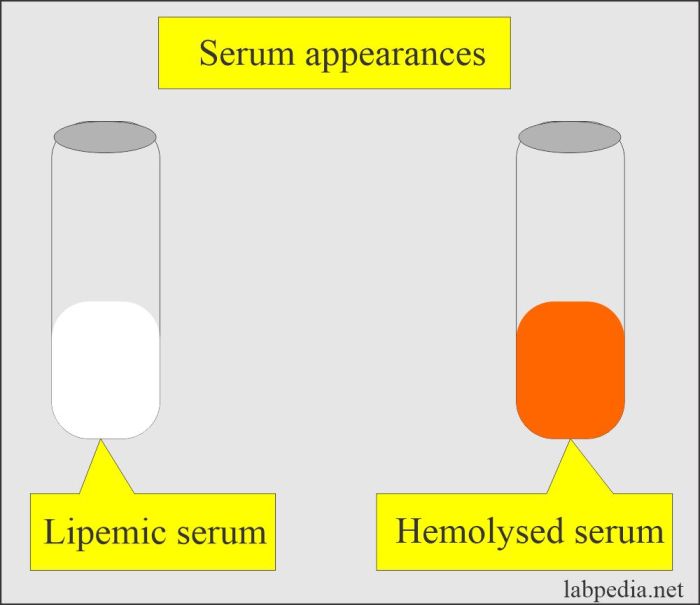
Assessing serum appearance is a crucial step in clinical diagnostics, providing valuable information about a patient’s health status. Various methods are employed to evaluate serum appearance, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Visual Inspection
Visual inspection is a simple and cost-effective method for assessing serum appearance. It involves observing the serum sample for clarity, color, and the presence of any visible particles or precipitates.
- Advantages:
- Rapid and inexpensive
- Can detect gross abnormalities
- Disadvantages:
- Subjective and prone to interobserver variability
- Limited sensitivity for detecting subtle changes
Step-by-Step Procedure:
- Place the serum sample in a clean glass tube or cuvette.
- Hold the tube or cuvette against a white background.
- Observe the sample for clarity, color, and any visible particles or precipitates.
- Record the observations.
Factors Affecting Serum Appearance

The appearance of serum can be affected by various factors during sample collection, storage, and handling. These factors can influence the accuracy of serum appearance assessment, leading to misinterpretation of results.
Sample Collection
- Hemolysis:Improper venipuncture or sample handling can cause red blood cell rupture, releasing hemoglobin into the serum, resulting in a red or pink appearance.
- Lipemia:High levels of triglycerides or chylomicrons in the serum can make it appear cloudy or milky, interfering with light transmission measurements.
- Icterus:Increased bilirubin levels can impart a yellow color to the serum, potentially masking other changes in appearance.
Storage
- Temperature:Extreme temperatures can alter protein solubility and precipitation, affecting serum clarity.
- Light exposure:Prolonged exposure to light can induce photooxidation of bilirubin, leading to a decrease in its yellow color.
Handling
- Centrifugation:Insufficient or excessive centrifugation can alter the distribution of particles in the serum, affecting its appearance.
- Pipetting:Using improper pipetting techniques can introduce air bubbles or disturb the sample, affecting its optical properties.
Precautions
To minimize the impact of these factors, it is essential to follow standardized protocols for sample collection, storage, and handling. These include using proper venipuncture techniques, maintaining appropriate storage temperatures, and avoiding prolonged light exposure. Additionally, using automated analyzers for serum appearance assessment can reduce variability and improve accuracy.
Clinical Significance of Serum Appearance

Serum appearance is clinically significant as it can provide valuable insights into the diagnosis and monitoring of various diseases. It can serve as a diagnostic marker for certain conditions and help monitor disease progression or response to treatment.
Serum Appearance as a Diagnostic Marker
Alterations in serum appearance can be indicative of specific diseases or pathological processes. For instance, lipemia (milky appearance) can be associated with hypertriglyceridemia, while hemolysis (reddish discoloration) may indicate intravascular hemolysis.
Serum Appearance in Disease Monitoring
Serum appearance can be used to monitor the progression of certain diseases. For example, in patients with liver disease, serum turbidity can indicate the severity of liver dysfunction, while clearing of turbidity may suggest improvement in liver function.
Limitations of Serum Appearance as a Diagnostic Tool
While serum appearance can provide valuable information, it has certain limitations as a diagnostic tool. It is important to note that serum appearance alone is not sufficient for a definitive diagnosis, and other laboratory tests or clinical findings should be considered for accurate interpretation.
FAQ Insights: Knowledge Drill 9-7 Serum Appearance
What is the significance of serum clarity?
Serum clarity can indicate the presence of abnormalities such as inflammation, infection, or hemolysis, which can aid in disease diagnosis.
How can spectrophotometry be used to assess serum appearance?
Spectrophotometry measures the absorbance of light at specific wavelengths, providing quantitative data on serum color and turbidity.
What factors can affect serum consistency?
Factors such as fibrinogen levels, viscosity, and the presence of lipoproteins can influence serum consistency, which can be assessed visually.

